Menu
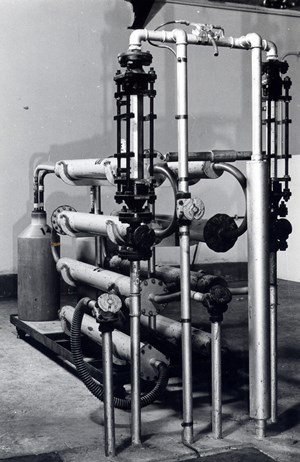
Gas absorption train
Credit: Willam McCallum F.I.I.P., F.R.P.S, F.R.S.A.
Digital Credit: Leah White
Publisher: None
Rights: Image Gallery user terms
Description: To measure oxygen consumption and carbon dioxide production in a closed circuit respiration chamber the chamber atmosphere is circulated through a gas absorption train. Air passes out of the chamber through the air pump and returns via three separate circuits, each circuit controlled by a diaphragm valve. Circuit one is a simple by-pass. Circuit two is the main circuit to absorb water and measure carbon dioxide production, as seen in the above image. Gas from the chamber first passes through three tubes containing silcica gel. The dry air then passes through two rigid polythene bottles containing 40% potassium hydroxide solution for the absorption of carbon dioxide. Water vapor blown out of the potash solution is absorbed by a further three tubes of silica gel. The change in weight of the potash bottles and the final three tubes of silica gel is the approximate weight of carbon dioxide produced by the animal. At the end of an experimental day this value is corrected for the carbon dioxide remaining in the chamber atmosphere by analyzing a sample of this gas. Knowing the volume of the chamber and this carbon dioxide percentage a correction can be calculated. The last circuit is a humidity control circuit consisting of two tubes of silica gel. The rate of passage of air through the circuits is controlled by the setting of three diaphragm valves and is indicated by two flowmeters. Removal of the carbon dioxide reduces the pressure in the chamber allowing oxygen to enter from the spirometer.
Resolution: 1024x1577
File Size: 1.23 MB
